sed 简明教程
 awk于1977年出生,今年36岁本命年,sed比awk大2-3岁,awk就像林妹妹,sed就是宝玉哥哥了。所以 林妹妹跳了个Topless,他的哥哥sed坐不住了,也一定要出来抖一抖。
awk于1977年出生,今年36岁本命年,sed比awk大2-3岁,awk就像林妹妹,sed就是宝玉哥哥了。所以 林妹妹跳了个Topless,他的哥哥sed坐不住了,也一定要出来抖一抖。
sed全名叫stream editor,流编辑器,用程序的方式来编辑文本,相当的hacker啊。sed基本上就是玩正则模式匹配,所以,玩sed的人,正则表达式一般都比较强。
同样,本篇文章不会说sed的全部东西,你可以参看sed的手册,我这里主要还是想和大家竞争一下那些从手机指缝间或马桶里流走的时间,用这些时间来学习一些东西。当然,接下来的还是要靠大家自己双手。
目录
用s命令替换
我使用下面的这段文本做演示:
$ cat pets.txt This is my cat my cat's name is betty This is my dog my dog's name is frank This is my fish my fish's name is george This is my goat my goat's name is adam
把其中的my字符串替换成Hao Chen’s,下面的语句应该很好理解(s表示替换命令,/my/表示匹配my,/Hao Chen’s/表示把匹配替换成Hao Chen’s,/g 表示一行上的替换所有的匹配):
$ sed "s/my/Hao Chen's/g" pets.txt This is Hao Chen's cat Hao Chen's cat's name is betty This is Hao Chen's dog Hao Chen's dog's name is frank This is Hao Chen's fish Hao Chen's fish's name is george This is Hao Chen's goat Hao Chen's goat's name is adam
注意:如果你要使用单引号,那么你没办法通过\’这样来转义,就有双引号就可以了,在双引号内可以用\”来转义。
再注意:上面的sed并没有对文件的内容改变,只是把处理过后的内容输出,如果你要写回文件,你可以使用重定向,如:
$ sed "s/my/Hao Chen's/g" pets.txt > hao_pets.txt
或使用 -i 参数直接修改文件内容:
$ sed -i "s/my/Hao Chen's/g" pets.txt
在每一行最前面加点东西:
$ sed 's/^/#/g' pets.txt #This is my cat # my cat's name is betty #This is my dog # my dog's name is frank #This is my fish # my fish's name is george #This is my goat # my goat's name is adam
在每一行最后面加点东西:
$ sed 's/$/ --- /g' pets.txt This is my cat --- my cat's name is betty --- This is my dog --- my dog's name is frank --- This is my fish --- my fish's name is george --- This is my goat --- my goat's name is adam ---
顺手介绍一下正则表达式的一些最基本的东西:
-
^表示一行的开头。如:/^#/以#开头的匹配。 -
$表示一行的结尾。如:/}$/以}结尾的匹配。 -
\<表示词首。 如:\<abc表示以 abc 为首的詞。 -
\>表示词尾。 如:abc\>表示以 abc 結尾的詞。 -
.表示任何单个字符。 -
*表示某个字符出现了0次或多次。 -
[ ]字符集合。 如:[abc]表示匹配a或b或c,还有[a-zA-Z]表示匹配所有的26个字符。如果其中有^表示反,如[^a]表示非a的字符
正规则表达式是一些很牛的事,比如我们要去掉某html中的tags:
<b>This</b> is what <span style="text-decoration: underline;">I</span> meant. Understand?
看看我们的sed命令
# 如果你这样搞的话,就会有问题 $ sed 's/<.*>//g' html.txt Understand? # 要解决上面的那个问题,就得像下面这样。 # 其中的'[^>]' 指定了除了>的字符重复0次或多次。 $ sed 's/<[^>]*>//g' html.txt This is what I meant. Understand?
我们再来看看指定需要替换的内容:
$ sed "3s/my/your/g" pets.txt This is my cat my cat's name is betty This is your dog my dog's name is frank This is my fish my fish's name is george This is my goat my goat's name is adam
下面的命令只替换第3到第6行的文本。
$ sed "3,6s/my/your/g" pets.txt This is my cat my cat's name is betty This is your dog your dog's name is frank This is your fish your fish's name is george This is my goat my goat's name is adam
$ cat my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam
只替换每一行的第一个s:
$ sed 's/s/S/1' my.txt ThiS is my cat, my cat's name is betty ThiS is my dog, my dog's name is frank ThiS is my fish, my fish's name is george ThiS is my goat, my goat's name is adam
只替换每一行的第二个s:
$ sed 's/s/S/2' my.txt This iS my cat, my cat's name is betty This iS my dog, my dog's name is frank This iS my fish, my fish's name is george This iS my goat, my goat's name is adam
只替换第一行的第3个以后的s:
$ sed 's/s/S/3g' my.txt This is my cat, my cat'S name iS betty This is my dog, my dog'S name iS frank This is my fiSh, my fiSh'S name iS george This is my goat, my goat'S name iS adam
多个匹配
如果我们需要一次替换多个模式,可参看下面的示例:(第一个模式把第一行到第三行的my替换成your,第二个则把第3行以后的This替换成了That)
$ sed '1,3s/my/your/g; 3,$s/This/That/g' my.txt This is your cat, your cat's name is betty This is your dog, your dog's name is frank That is your fish, your fish's name is george That is my goat, my goat's name is adam
上面的命令等价于:(注:下面使用的是sed的-e命令行参数)
sed -e '1,3s/my/your/g' -e '3,$s/This/That/g' my.txt
我们可以使用&来当做被匹配的变量,然后可以在基本左右加点东西。如下所示:
$ sed 's/my/[&]/g' my.txt This is [my] cat, [my] cat's name is betty This is [my] dog, [my] dog's name is frank This is [my] fish, [my] fish's name is george This is [my] goat, [my] goat's name is adam
圆括号匹配
使用圆括号匹配的示例:(圆括号括起来的正则表达式所匹配的字符串会可以当成变量来使用,sed中使用的是\1,\2…)
$ sed 's/This is my \([^,&]*\),.*is \(.*\)/\1:\2/g' my.txt cat:betty dog:frank fish:george goat:adam
上面这个例子中的正则表达式有点复杂,解开如下(去掉转义字符):
正则为:This is my ([^,]*),.*is (.*)
匹配为:This is my (cat),……….is (betty)
然后:\1就是cat,\2就是betty
sed的命令
让我们回到最一开始的例子pets.txt,让我们来看几个命令:
N命令
先来看N命令 —— 把下一行的内容纳入当成缓冲区做匹配。
下面的的示例会把原文本中的偶数行纳入奇数行匹配,而s只匹配并替换一次,所以,就成了下面的结果:
$ sed 'N;s/my/your/' pets.txt This is your cat my cat's name is betty This is your dog my dog's name is frank This is your fish my fish's name is george This is your goat my goat's name is adam
也就是说,原来的文件成了:
This is my cat\n my cat's name is betty This is my dog\n my dog's name is frank This is my fish\n my fish's name is george This is my goat\n my goat's name is adam
这样一来,下面的例子你就明白了,
$ sed 'N;s/\n/,/' pets.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam
a命令和i命令
a命令就是append, i命令就是insert,它们是用来添加行的。如:
# 其中的1i表明,其要在第1行前插入一行(insert) $ sed "1 i This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong" my.txt This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam # 其中的1a表明,其要在最后一行后追加一行(append) $ sed "$ a This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong" my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam
我们可以运用匹配来添加文本:
# 注意其中的/fish/a,这意思是匹配到/fish/后就追加一行 $ sed "/fish/a This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong" my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong This is my goat, my goat's name is adam
下面这个例子是对每一行都挺插入:
$ sed "/my/a ----" my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty ---- This is my dog, my dog's name is frank ---- This is my fish, my fish's name is george ---- This is my goat, my goat's name is adam ----
c命令
c 命令是替换匹配行
$ sed "2 c This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong" my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam $ sed "/fish/c This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong" my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my monkey, my monkey's name is wukong This is my goat, my goat's name is adam
d命令
删除匹配行
$ sed '/fish/d' my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my goat, my goat's name is adam $ sed '2d' my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam $ sed '2,$d' my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty
p命令
打印命令
你可以把这个命令当成grep式的命令
# 匹配fish并输出,可以看到fish的那一行被打了两遍, # 这是因为sed处理时会把处理的信息输出 $ sed '/fish/p' my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my fish, my fish's name is george This is my goat, my goat's name is adam # 使用n参数就好了 $ sed -n '/fish/p' my.txt This is my fish, my fish's name is george # 从一个模式到另一个模式 $ sed -n '/dog/,/fish/p' my.txt This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george #从第一行打印到匹配fish成功的那一行 $ sed -n '1,/fish/p' my.txt This is my cat, my cat's name is betty This is my dog, my dog's name is frank This is my fish, my fish's name is george
几个知识点
好了,下面我们要介绍四个sed的基本知识点:
Pattern Space
第零个是关于-n参数的,大家也许没看懂,没关系,我们来看一下sed处理文本的伪代码,并了解一下Pattern Space的概念:
foreach line in file {
//放入把行Pattern_Space
Pattern_Space <= line;
// 对每个pattern space执行sed命令
Pattern_Space <= EXEC(sed_cmd, Pattern_Space);
// 如果没有指定 -n 则输出处理后的Pattern_Space
if (sed option hasn't "-n") {
print Pattern_Space
}
}
Address
第一个是关于address,几乎上述所有的命令都是这样的(注:其中的!表示匹配成功后是否执行命令)
[address[,address]][!]{cmd}
address可以是一个数字,也可以是一个模式,你可以通过逗号要分隔两个address 表示两个address的区间,参执行命令cmd,伪代码如下:
bool bexec = false
foreach line in file {
if ( match(address1) ){
bexec = true;
}
if ( bexec == true) {
EXEC(sed_cmd);
}
if ( match (address2) ) {
bexec = false;
}
}
关于address可以使用相对位置,如:
# 其中的+3表示后面连续3行 $ sed '/dog/,+3s/^/# /g' pets.txt This is my cat my cat's name is betty # This is my dog # my dog's name is frank # This is my fish # my fish's name is george This is my goat my goat's name is adam
命令打包
第二个是cmd可以是多个,它们可以用分号分开,可以用大括号括起来作为嵌套命令。下面是几个例子:
$ cat pets.txt
This is my cat
my cat's name is betty
This is my dog
my dog's name is frank
This is my fish
my fish's name is george
This is my goat
my goat's name is adam
# 对3行到第6行,执行命令/This/d
$ sed '3,6 {/This/d}' pets.txt
This is my cat
my cat's name is betty
my dog's name is frank
my fish's name is george
This is my goat
my goat's name is adam
# 对3行到第6行,匹配/This/成功后,再匹配/fish/,成功后执行d命令
$ sed '3,6 {/This/{/fish/d}}' pets.txt
This is my cat
my cat's name is betty
This is my dog
my dog's name is frank
my fish's name is george
This is my goat
my goat's name is adam
# 从第一行到最后一行,如果匹配到This,则删除之;如果前面有空格,则去除空格
$ sed '1,${/This/d;s/^ *//g}' pets.txt
my cat's name is betty
my dog's name is frank
my fish's name is george
my goat's name is adam
Hold Space
第三个我们再来看一下 Hold Space
接下来,我们需要了解一下Hold Space的概念,我们先来看四个命令:
g: 将hold space中的内容拷贝到pattern space中,原来pattern space里的内容清除
G: 将hold space中的内容append到pattern space\n后
h: 将pattern space中的内容拷贝到hold space中,原来的hold space里的内容被清除
H: 将pattern space中的内容append到hold space\n后
x: 交换pattern space和hold space的内容
这些命令有什么用?我们来看两个示例吧,用到的示例文件是:
$ cat t.txt one two three
第一个示例:
$ sed 'H;g' t.txt one one two one two three
是不是有点没看懂,我作个图你就看懂了。
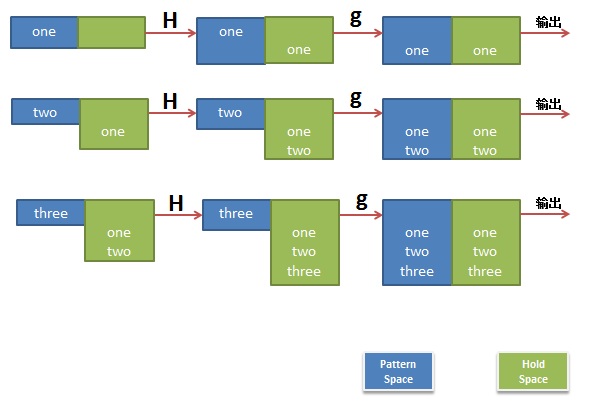
第二个示例,反序了一个文件的行:
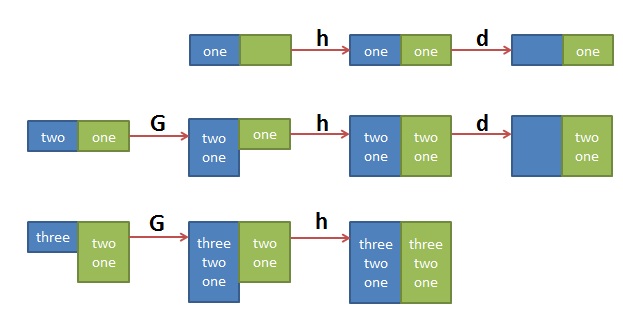
$ sed '1!G;h;$!d' t.txt three two one
其中的 ‘1!G;h;$!d’ 可拆解为三个命令
- 1!G —— 只有第一行不执行G命令,将hold space中的内容append回到pattern space
- h —— 第一行都执行h命令,将pattern space中的内容拷贝到hold space中
- $!d —— 除了最后一行不执行d命令,其它行都执行d命令,删除当前行
这个执行序列很难理解,做个图如下大家就明白了:
就先说这么多吧,希望对大家有用。
(全文完)
(转载本站文章请注明作者和出处 酷 壳 – CoolShell ,请勿用于任何商业用途)







 (122 人打了分,平均分: 4.61 )
(122 人打了分,平均分: 4.61 )
《sed 简明教程》的相关评论
跟着学习
在工作中(web log数据挖掘)中经常使用shell+awk+sed+hadoop streaming,很方便
想知道浩哥写这些文章的时间都是从哪挤出来的了,手指缝还是马桶上:)
和 AWK 一起学了!注意到 AWK 正确写法是全部大写的,sed 则是小写。
看到了N命令, 我实验了下, 结果如下:
/home/wangrui/command_test/sed_test>sed ‘N;s/my/your/’ rei
This is your cat
your cat’s name is betty
This is your dog
your dog’s name is frank
This is your fish
your fish’s name is george
This is your goat
your goat’s name is adam
/home/wangrui/command_test/sed_test>sed ‘N;s/\n/,/’ rei
This is your cat, my cat’s name is betty
This is your dog, my dog’s name is frank
This is your fish, my fish’s name is george
This is your goat, my goat’s name is adam
不太明白为什么我的结果跟博主的不同.
再贡献两个链接,讲sed的。
http://www.chinabin.cn/code-space/shell/2150.html
http://sed.sourceforge.net/sed1line_zh-CN.html
学习了,很强大
sed ‘s///g’ html.txt
meant. Understand?
写的很不错,基本涵盖所有的sed内容,标签之类的未提到
sed ‘s///g’ html.txt 这个的结果是:
meant. Understand?
看完了, 每个用法都有相应的例子, 学起来可以动动手增强记忆.
sed 确实是文字处理的神器.
谢谢~
@Dragon 用的shell不一样吧
a命令和i命令 有一处写错啦。
$ sed “$ a This is my monkey, my monkey’s name is wukong” my.txt
应该是 sed “1 a This is my monkey, my monkey’s name is wukong” my.txt
“先来看N命令 —— 把下一行的内容纳入当成缓冲区做匹配。”,“当成”是不是应该为“当前”?
@Dragon
用的shell是bash吗
sed ‘H;g’ t.txt
这个命令的输出,第一行应该是空的,像图里画的那样。
这算不算sed的一个bug?
当my.txt内容:
dog
fishe
goat
fishe
goat
执行命令sed -n ‘/dog/,/goat/p’ my.txt结果为:
dog
fishe
goat
当my.txt内容为:
dog
fishe
goat
dog #goat后面多了一个dog
fishe
goat
执行命令sed -n ‘/dog/,/goat/p’ my.txt结果为:
dog
fishe
goat
dog
fishe
goat
对应sed源码是:
bool bexec = false
foreach line in file {
if ( match(address1) ){
bexec = true;
}
if ( bexec == true) {
EXEC(sed_cmd);
}
if ( match (address2) ) {
bexec = false;
}
}
是否应该改写成:
bool bexec = false
foreach line in file {
if ( match(address1) ){
bexec = true;
}
if ( bexec == true) {
EXEC(sed_cmd);
}
if ( match (address2) ) {
bexec = false;
break; #break
}
}
lz 的图是用什么作的呢?不是 excel 吧。
@Dragon
看你的rei文件内容,应该是
This is your cat
my cat’s name is betty
This is your dog
my dog’s name is frank
This is your fish
my fish’s name is george
This is your goat
my goat’s name is adam
与博主的文件内容不同,当然结果不同了
hold space只是在两次处理cycles间临时可以用于保存内容的buffer,必要时以避免pattern space第一次处理后的结果被第二次读取覆盖。学习了。感谢博主。
@seesea
更像是PPT之类的东西
最后的图比较精彩,一图胜千言啊
下回可否介绍下技术博客的写作,如何做图以说清楚问题
以前还以为什么Linux下的命令行工具都是鸡肋,现在觉得比word都好用了…
难道对会用的人来说是鸡腿,不会用的就是鸡肋?
感谢送鸡腿…..
在学习一把
原来VIM的替换命令的语法和sed的语法是一样的。:-o
# 如果你这样搞的话,就会有问题
$ sed ‘s///g’ html.txt
Understand?
# 要解决上面的那个问题,就得像下面这样。
# 其中的'[^>]’ 指定了除了>的字符重复0次或多次。
$ sed ‘s/]*>//g’ html.txt
This is what I meant. Understand?
sed “s///g” html.txt为什么这样不行,只能将第一个去掉,不再匹配后面的
sed “s/\//g” html.txt
问号取消贪婪匹配,评论中不能显示
很不错,特意来支持博主
真佩服那个时代的程序员,哪时候写程序和调试程序远没有现在这么方面,但那些大神们却发明了这么多这么好用的工具。跟人家相比自己写的程序就是渣
来晚了,一直等这篇文章。
个人觉得这篇没有AWK那篇写的好。
用了那么久的sed, hold space是第一次听说, 真是惭愧, 感谢博主点拨
@wang
shell还对命令有影响啊? 我用的tcsh
@ving zhang
我给了两个例子, 第二个跟博主的结果一样, 第一个不同, 用的文本是同一个
@ving zhang
你的想法错了, 我用的跟博主是一样的, 偶数行前面带空格. 即使没空格也没影响把, 我毕竟没处理空格
学习了,总结的非常好.
完全干货,收了!
@小小虎
or use ‘$’ to append a new line after last line:
sed “$ a This is my monkey, my monkey’s name is wukong” my.txt
errata:
h —— 第一行都执行h命令
–>
h —— 每一行都执行h命令
留着,备用
@ruiqi
你的理解有误 “p”是打印所有被匹配的模式 而不仅仅是打印第一次被匹配的 如果只打印第一次匹配的话可以这样用:
$ sed -n ‘1,/goat/{/dog/,/goat/p}’ my.txt
首先从第一行匹配到第一次出现goat的那行
之后再在其中匹配从dog到goat的中间行
@COSTA_NA
oops, this expression does not work also.
只替换第一行的第3个以后的s:
$ sed ‘s/s/S/3g’ my.txt
—— 这个应该是替换每一行的第三个“s”字母吧?!
看起来很吃力.不知道为何.能不能讲解一下java,c++简明教程.还有shell简明教程.
在Mac下面,因为貌似不是GNU的sed,于是i和a命令用起来都很诡异。。。
@long904
后面还有个g呢。
如果只替换每一行的第三个,应该这样写:
sed ‘s/s/S/3’ my.txt
大婶,能不能提供点关于阅读linux内核的方法???
好文,总结很系统。
有个笔误:“\ 表示以 abc 結尾的詞”应该是\>表示词尾
图示很好。对patten space和hold space概念更清晰了。谢谢分享!